Year: II
BASIC PERIODONTOLOGY 1
Theory: 4 hrs. /week Full Marks: (Th. 100 + Pr. 100)
Practical: 4 hrs. /week Pass Marks: (Th. 40 + Pr. 50)
Course Description
The course introduces the students to basic knowledge and skill necessary to use plaque control measures on patients; educate and motivate them for maintaining oral Science. It teaches the students to identify and use of periodontal instruments for scaling, and maintenance of periodontal instruments, then refer the conditions which require specialized dental care.
Objectives:
On completion of the course the learner will be able to:
- Acquire knowledge and skill to perform various plaque control methods and use of oral Science aids on patients in clinical setting and in the community
- Describe periodontal health, and determinants of periodontal disease
- Record various gingival and periodontal indices
- Identify and use periodontal instruments with manual dexterity
- Perform dental scaling using manual and ultra sonic instruments
- Maintenance of periodontal instruments
- Refer the patients who require further treatment
Unit 1: Introduction: [8]
- Definition of Periodontology/Periodontics
- Describe Periodontium
- Historical background of Periodontology
- Scope of Periodontics
Unit 2: Normal Periodontium [35]
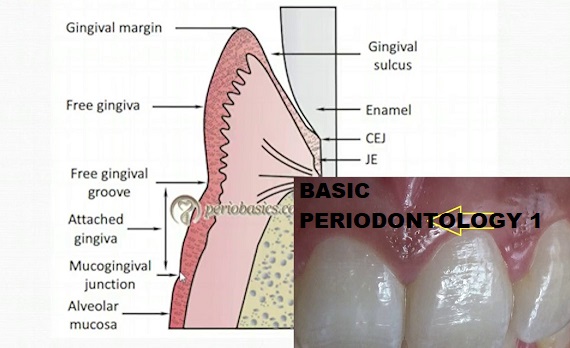
Sub unit 1: Gingiva
- Definition of gingiva
- Normal clinical features of gingiva
- Normal microscopic features of gingiva
- Gingival connective tissue & gingival fibres with illustrations
- Development of gingival sulcus
- Renewal of gingival epithelium
- Blood supply, lymphatic drainage and nerve supply of gingiva
- Correlation of normal clinical and microscopic features of gingiva
Sub unit 2: Periodontal ligament
- Definition of periodontal ligament
- Enlist periodontal ligament fibers with illustrations
- Various cellular elements & ground substance
- Functions of periodontal ligament
Sub unit 3: Cementum
- Concept of cementum and its structure
- Classification and types of cementum
- Cemento-enamel junction
- Thickness of cementum
- Cementum resorption and repair
- Ankylosis
Sub unit 4: Alveolar process
- Definition and structure of alveolar process
- Cells, intercellular matrix
- Bone marrow, periosteum and endosteum in alveolar process
- Socket wall, interdental septum
- Normal osseous topography of alveolar bone
- Fenestration and dehiscence
- Remodeling of alveolar bone
- Physiologic migration of the teeth
- Occlusal forces and the periodontium
- Blood supply, venous & lymphatic drainage
Sub unit 5: Defense mechanism in periodontal health
- Role of epithelium
- Gingival crevicular fluid in defense mechanism of oral cavity
- Role of saliva and its function
Unit 3: Classification and epidemiology of periodontal disease [20]
Sub unit 1: Classification of periodontal disease
- Classify gingival and periodontal diseases as described in World Workshop on Periodontal Health 1999
- Advantage and limitations of World Workshop classification
Sub unit 2: Epidemiology of periodontal disease
- Definition: Epidemiology, prevalence, incidence, index
- Discuss epidemiology of periodontal disease
- Discuss prevalence and incidence of periodontal disease
- Enlist indices used in periodontics
- Describe Periodontal index
- Describe Gingival index
- Describe Oral Hygiene index
- Describe CPITN
- Describe plaque index
Unit 4: Etiology of periodontal disease [33]
Sub unit 1: Dental plaque
- Definition of dental plaque
- Structure and composition of dental plaque
- Formation of dental plaque
- Structure and physiologic properties of dental plaque
- Role of dental plaque in periodontal disease
Sub unit 2: Periodontal microbiology
- Microbiology of dental plaque
- Association of plaque microorganisms with periodontal disease
- Microbial specificity of periodontal disease
- Criteria for identification of periodontal pathogens
- Virulence factor of periodontal pathogens
- Colonization and invasion of periodontal tissues
- Mechanism of host tissue damage
Sub unit 3: Host response
- Mechanism of inflammatory cell response
- Role of mast cells, neutrophils, macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells
- Role of antibody, complement, cytokines and immune mechanisms
Sub unit 4: Dental calculus
- Definition and classification of dental calculus
- Composition of dental calculus
- Mechanism of formation of dental calculus
- Mechanism of attachment of calculus to tooth surface
- Theories regarding the mineralization of calculus
- Etiologic significance of dental calculus
Sub unit 5: Local deposits and its role in oral Science
- Describe materia alba
- Describe dental stain
- Describe food debris
Sub unit 6: Role of iatrogenic factors
- Role of margin of restoration, contact point, surface roughness, overhanging restoration, tooth contours
- Role faulty dental materials and design of dentures
- Periodontal problems associated with faulty orthodontic treatment
Sub unit 7: Effects of local factors
- Effects of unreplaced missing teeth
- Effects of mouth breathing
- Effects of tongue thrusting
- Effects of bruxism
- Effects of tooth brush trauma
- Effects of chemical irritation
- Effects of radiation
Sub unit 8: Influence of systemic disease on oral health
- Influence of nutritional deficiencies on periodontium
- Influence of endocrine disease on periodontium
- Influence of hematological disease on periodontium
- Influence of immunological disorders on periodontium
- Influence of cardiovascular disease on periodontium
- Influence of psychosomatic disorderson periodontium
Sub unit 9: AIDS and periodontium
- Oral and periodontal manifestations of HIV infection
- Oral hairy leukoplakia
- Oral candidiasis
- Kaposi sarcoma
- Bacillary angiomatosis
- Oral hyperpigmentation
- Atypical ulcers and delayed healing
- HIV gingivitis and periodontitis
Sub unit 10: Age changes in Periodontium
- General effects of aging
- Ageing related changes in the periodontium
- Masticatory efficiency in aging
- Ageing and cumulative effects of oral disease
Unit 5: Plaque Control [30]
Sub unit 1: Introduction
- Importance of oral hygiene and its effect on general health
- Plaque control measures and its significance
- Classification of plaque control methods
- Personal oral hygiene methods
- Importance of patient education on plaque control
- Use of disclosing agents
Sub unit 2: Tooth brush & Dentifrice
- Concept and types of tooth brush
- Use of powdered tooth brush
- Dentifrices and its composition
- Composition & mechanism of action of fluoridated toothpastes
- Composition & mechanism of action of desensitizing toothpastes
- Various types of tooth brushing methods and their significance in different patients
Sub unit 3: Inter-dental cleaning aids
- Use of toothpick
- Use of dental floss
- Use of inter-dental brushes, ortho brushes
- Use of gum massage/gum stimulator
Sub unit 4: Chemical plaque control methods
- Describe and classify various chemical plaque control agents
- Mechanism of action of various plaque control agents
Sub unit 5: Oral irrigation device
- Use of oral irrigation device
- Use of periodontal pocket irrigation
- Use of home irrigation devices
- Instruments and medicaments used in oral irrigation
Unit 6: Periodontal Instruments & Instrumentation [30]
Sub unit 1: Periodontal instruments
- Describe instrument design and classification
- Describe various diagnostic instruments
- Describe various manual periodontal instruments
- Describe various scalers, currets and root planing instruments
- Describe sonic, ultrasonic & piezo-electric scalers
Sub unit 2: Principles of instrumentation
- Describe anatomic descriptions and considerations during periodontal instrumentation
- Describe patient and operator position
- Describe instrument grasp
- Describe establishing finger rests
- Describe instrument angulations, activation and adaptation
- Describe various strokes of using manual instruments
Sub unit 3: Instrument sharpening
- Principles and objective of sharpening
- Various sharpening stones and material
- Sharpening of manual periodontal instruments
- Teacher: laxman poudel
